
IN A RETROSPECTIVE COHORT STUDY OF US EHR DATA
FOR PATIENTS WITH CKD NOT ON DIALYSIS WHO HAVE Hb < 10 g/dL*
for patients with CKD not on dialysis who have Hb < 10 g/dL*
In a retrospective cohort study of US EHR data for patients with CKD not on dialysis who have Hb < 10 g/dL*
The KDIGO® Clinical Practice Guideline for Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease (2012) recommends that for patients with Hb < 10 g/dl, the decision whether to initiate ESA therapy be individualized based on the rate of fall of Hb concentration, prior response to iron therapy, the risk of needing a transfusion, the risks related to ESA therapy, and the presence of symptoms attributable to anemia.3
*14,922 adults with eGFR results > 10 and <60 mL/min/1.73 m2; average follow-up was 1.96 years; anemia defined as hb ≤ 10 g/dL.
†IV iron, epoetin alfa, darbepoetin alfa, polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta, or RBC transfusion.
EHR = electronic health record; NOD = not on dialysis.
KDIGO® is a registered trademark of Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes.

‡Of the 14,922 adults with eGFR results > 10 and < 60ml/min/1.732, 7140 were treated; average follow-up was 1.96 years; anemia defined as Hb ≤ 10 g/dL.
DPO = darbepoetin alfa; EPO = epoetin alfa.
ALLOSENSITIZATION
TRANSFUSION REACTIONS
VOLUME OVERLOAD
IRON OVERLOAD
HYPERKALEMIA
TRANSMISSION OF INFECTIONS
The KDIGO® Clinical Practice Guideline for Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease (2012) recommends avoiding, when possible, red cell transfusions to minimize the general risks related to their use.3
KDIGO® is a registered trademark of Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes.

ARANESP® can be used to reduce the need for RBC transfusion in your CKD-NOD patients with Hb < 10 g/dL.4
Compared with Hb ≥ 11.0 g/dL the start of hemodialysis:


*N = 4604 hemodialysis patients from 21 countries in DOPPS phases 4-5 (2009-2011); anemia defined as Hb < 10 g/dL.

*N=22,643 hemodialysis patients from 20 countries in DOPPS phases 5-7 (2012-2022).
Hb levels maintained over time with monthly dosing
Hb levels maintained over time with monthly dosing
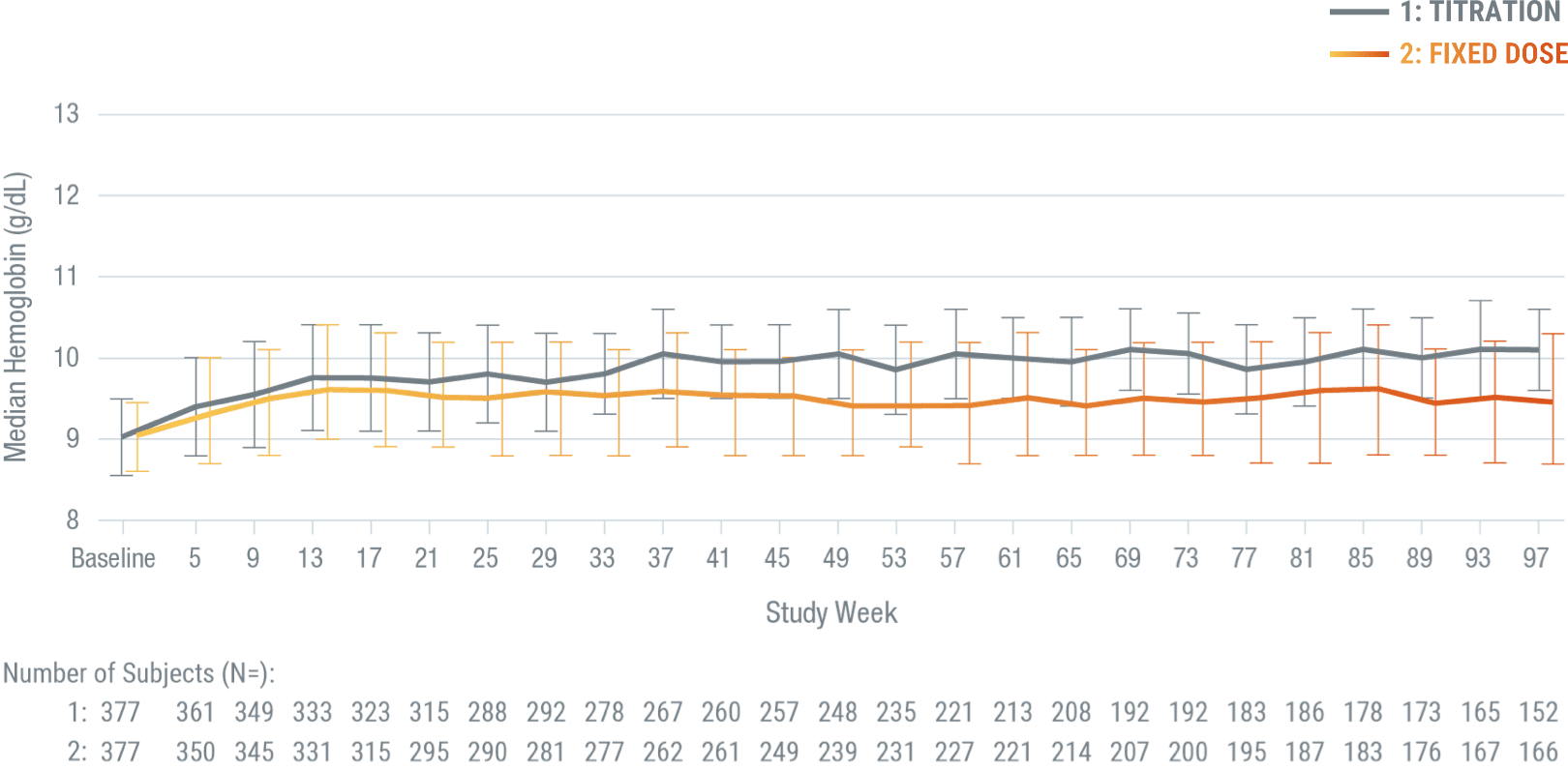

ARANESP® achieved median Hb concentrations of 9.9 g/dL in patients who received a titrated dose and 9.4 g/dL in patients who received a fixed dose.
*A double-blind, parallel-group phase 3 trial involving 756 adults with stage 3 to 5 CKD and anemia (Hb < 10.0 g/dL) randomized to receive ARANESP® given as a fixed dose (N = 379) versus administered according to a hemoglobin-based, titration-dose algorithm (N = 377), for up to 2 years. In the hemoglobin-based, titration-dose group, ARANESP® doses were titrated to maintain Hb ≥ 10.0 g/dL, with dose reduction if Hb exceeded 10.5 g/dL or if the Hb rise exceeded 1.0 g/dL over 4 weeks. In the fixed dose group, patients received a fixed dose of ARANESP® (0.45 mg/kg). All patients received ARANESP® as a subcutaneous injection once every 4 weeks. Patients received transfusions as deemed necessary by the treating physician.
*Refer to ARANESP® full Prescribing Information for additional detail on dosing in patients with CKD, including those on dialysis and pediatric patients (less than 18 years).
INITIATION
Consider initiating ARANESP® treatment only when the Hb level is < 10 g/dL and the following considerations apply:
Q4W recommended starting dose: 0.45 mcg/kg body weight as an IV or SC injection once at 4-week intervals as appropriate.
MONITORING
Following initiation of therapy and after each dose adjustment, monitor Hb at least weekly until the Hb is stable and sufficient to minimize the need for RBC transfusion.
DOSE ADJUSTMENTS
When adjusting therapy, consider Hb rate of rise, rate of decline, ESA responsiveness, and Hb variability:
REDUCE OR INTERRUPT DOSE
If Hb rises rapidly (eg, more than 1 g/dL in any 2-week period), reduce the dose by 25% or more, as needed, to reduce rapid responses.
If the Hb level exceeds 10 g/dL, reduce or interrupt the dose of ARANESP®, and use the lowest dose of ARANESP® sufficient to reduce the need for RBC transfusions.
INCREASE DOSE
If the Hb has not increased by more than 1 g/dL after 4 weeks of therapy, increase the dose by 25% when appropriate.
Patients with CKD and an insufficient Hb response to ESA therapy or a rate of Hb rise of > 1 g/dL over 2 weeks may be at an even greater risk for cardiovascular reactions and mortality than other patients.
Q4W = every 4 weeks; SC = subcutaneous.


Available as a prefilled syringe.
Extended dosing* with proven hemoglobin control
*Due to the longer serum half-life, ARANESP® should be administered less frequently than epoetin alfa. ARANESP® should be administered once a week (QW) if a patient was receiving epoetin alfa 2 to 3 times weekly.
ARANESP® should be administered once every 2 weeks (Q2W) if a patient was receiving epoetin alfa once per week.
References:
ARANESP® (darbepoetin alfa) Important Safety Information, including Boxed WARNINGS
WARNING: ESAs INCREASE THE RISK OF DEATH, MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION, STROKE, VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM, THROMBOSIS OF VASCULAR ACCESS AND TUMOR PROGRESSION OR RECURRENCE
Chronic Kidney Disease:
Cancer:
Please see ARANESP® full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNINGS and Medication Guide.
ARANESP® (darbepoetin alfa) Important Safety Information, including Boxed WARNINGS
WARNING: ESAs INCREASE THE RISK OF DEATH, MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION, STROKE, VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM, THROMBOSIS OF VASCULAR ACCESS AND TUMOR PROGRESSION OR RECURRENCE
Chronic Kidney Disease:
Cancer:
Please see ARANESP® full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNINGS and Medication Guide.